Periodontology is a branch of medical dentistry dealing with health of the tooth supporting structures (periodontium). Periodontium is composed of gingiva, bones and connective tissues which tie the tooth to the bone (periodontal attachment). Gingivitis is an inflammatory change in the gingiva, and if the inflammation further develops, then it becomes periodontitis. Statistics have shown that 30% to 40% of people suffer from this disease, which is also one of the most frequent causes of teeth loss in adults.
What are periodontal diseases?
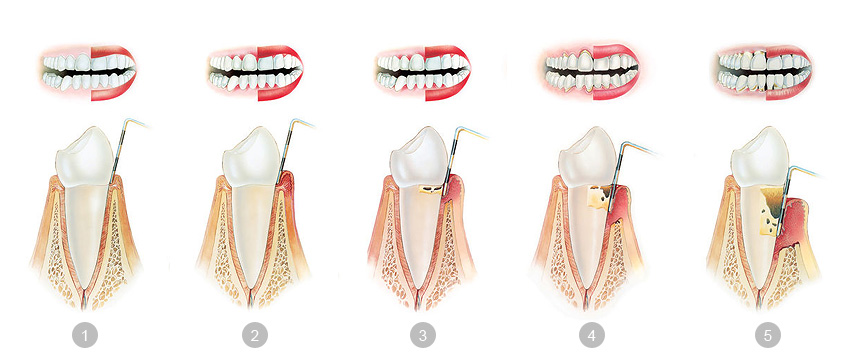
Periodontal diseases are inflammatory conditions leading to damage of the tissue which supports teeth. The first stage of the inflammation (gingive) is called gingivitis and can be completely cured. The first symptom of the disease is gum inflammation causing the gum to be red, swollen and sore, and it bleeds when brushing. Gingivitis is a treatable disease, and although the gum is more sensitive, there is still no loss of the soft and bone tissue. If the disease is not treated, the inflammation spreads to the second phase, periodontitis (periodontal disease), acute infection covering gingiva and the supporting bone, which can lead to the complete tooth loss in the end. Periodontitis is a silent disease, with usually mild symptoms until its progression. Main symptoms include gingiva inflammation and swelling, formation of pockets, gum recession, tooth mobility and bad breath as well.
Cause of periodontal disease
Main cause of periodontal disease is accumulation of dental plaque and bacteria. Toxins and poisons produced by the bacteria cause the infection which destroys the connective tissue, causing the recession of gingiva and formation of periodontal pockets in which food remains, causing further bacteria accumulation. Spread of the infection causes destruction of bone and connective tissue, parts of the supporting structure of the tooth which holds the tooth in place, and eventually can lead to a tooth falling out. The disease is usually a reflection of bad oral hygiene, as well as certain genetic predispositions, bad immune system and medication. Inadequate dental fillings and poorly prepared prosthetics can often cause plaque to accumulate in places which are difficult to reach. Periodontal diseases can occur as a consequence of certain systematic diseases (diabetes, leukaemia, AIDS, etc.) or certain bad habits such as smoking cigarettes.
Periodontal disease treatment
After the examination and analysis of the condition by using radiographic images, a periodontal specialist prepares a treatment plan. The treatment of a certain periodontal disease depends on its type and degree of development, and we can usually distinguish between the gingivitis treatment and periodontitis treatment. The objective of each treatment is to eliminate bacteria as the main cause of the inflammation.
Gingivitis
The procedure of treating gingivitis includes removing the dental plaque and the stone above the level of gingiva. The treatment is a combination of personal oral that includes correct brushing techniques, antiseptic liquids, dental floss and interdental brushes in order to remove the soft part of dental sediment –plaque. Professional cleaning is carried out after that, in order to remove hard sediments (stone) which are impossible to remove by brushing. Different manual and mechanical instruments are used for professional cleaning, breaking the dental stone structure and enabling its thorough removal.
Periodontitis
Treating periodontitis includes the removal of soft and hard sediments placed deeply in the periodontal pocket, which makes the treatment more complex and longer than treating gingivitis. Unlike gingivitis, treating periodontitis requires reaching below the level of gingiva, deep into the pockets. Gingivitis is an integral part of periodontitis, so before cleaning the pockets, it is necessary to eliminate the inflammation of gingiva. After taking care of gingivitis, the next step is to clean plaque and stone on surface of the dental root below the level of gingiva. Surgical methods are needed when the disease has progressed to such an extent that it requires the reduction of periodontal pockets, regeneration of tissue and bones using biologically compatible material or bone substitute materials. Surgical procedures are used when there is a need to reshape the gingiva in order to prevent its further recession, extend the tooth crown and transplant the bone and connective tissue.
How to prevent the occurrence of periodontal diseases?
Regular and correct maintenance of oral hygiene can reduce the risk of periodontitis. Regular checks at the dentist are recommended every 6 months and regular professional ultrasound cleaning of soft and hard teeth sediments, as well as teeth polishing. People who have diabetes should take special care about the cavity hygiene.
Crown extension
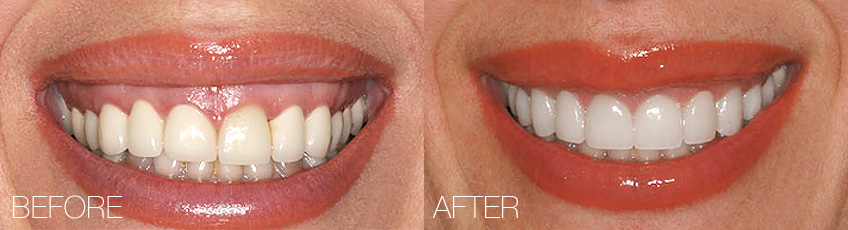
The condition of the gum can significantly influence the harmony and beauty of the smile. The gum should follow the smile line for the appearance to be harmonious. If gums are too much visible, even healthy teeth can look too short and chubby, causing the “gummy smile”.
These photographs show the real condition before and after the procedure. The results of each procedure are subject to individualities and normal variability of surgical results. Consequently, Bagatin Clinic cannot guarantee equal results for each individual client.
This problem can be solved by a small procedure which extends the crown of the natural tooth, removes excessive gum tissue, and even part of the bone surrounding the tooth in order to widen the surface of the visible tooth part and achieve more beautiful smile.
Free online consultation with our doctors
Send enquiryFeel free to contact us
By phone on +385 1 46 10 225 or through our online contact form
Send enquiry
Locations
| Green Gold Tower Ul. Grada Vukovara 269a/10, 10000 Zagreb |
|
| Donji grad Frana Folnegovića 1c/1, 10000 Zagreb |
|
| Dioklecijan Hotel & Residence Kranjčevićeva 45/1, 21000 Split |
Where to park
| Parking available in Green Gold centre, Zagreb underground garage. For detailed information download a map |